-
Five years ago, the coronavirus pandemic upended life for millions of people around the world. And it had an impact on Colorado’s economic landscape in ways that still linger today. We talk with a CU Boulder economist about how COVID changed the state’s economy, today on In The NoCo.
-
The humidity of where you live can play a big role in how long airborne viruses can survive. CU Boulder researchers found coronavirus particles released in a low-humidity environment remained infectious for twice as long as those in a more humid chamber.
-
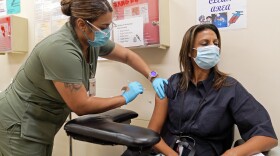
The new approach would simplify vaccination guidance so that, every fall, people would get a new shot, updated to try to match whatever variant is dominant.
-
Two reports from the CDC provided details on which groups have the highest death rates and which states are seeing the largest numbers.
-
New Department of Education data out Monday shows that student math and reading scores have suffered over the last few years. Between 2019 and this year, data shows that fourth and eighth grade scores suffered the most in math, but reading scores also took a hit.
-
Here we go again. The virus is starting to surge in many European countries and there are early signs a wave may be starting in the U.S. too.
-
The number of women in the workforce has finally returned to pre-pandemic levels, which is good for the economy. But after time away from the job market some women are reassessing their priorities.
-
Biden's comments — made as officials try to convince Americans to get a new booster shot and the White House seeks $22 billion in new COVID funding — were "unfortunate," several epidemiologists said.
-
They argue the threat posed by COVID has lessened because of preexisting immunity and access to treatment. Plus, some deaths may be incorrectly blamed on COVID. Others caution it's too soon to tell.
-
A new study suggests that. yes, there are superdodgers. But explaining why they've been able to avoid the virus is a bit complicated.

Play Live Radio
Next Up:
0:00
0:00
Available On Air Stations